R&D
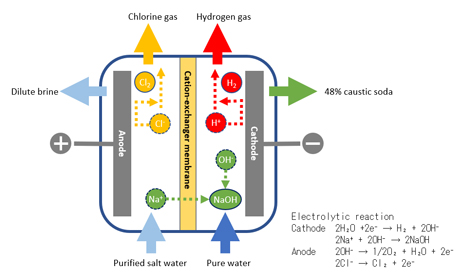
Salt water electrolysis
By electrolyzing brine, caustic soda, chlorine, and hydrogen can be produced.
Tokuyama started its salt water electrolysis business in 1952, and since 1985, we have been using ion-exchange membrane electrolyzers using our original zero-gap technology.
We are currently developing the world's most energy-efficient salt electrolyzers to help realize a carbon-free society.
External view of Tokuyama's salt electrolyzer


History of Tokuyama's salt water electrolysis business
| Year | Events |
|---|---|
| 1952 |
Start of mercury process salt water electrolysis business Power consumption rate (including incidental facilities): 3900 kWh/t-100% NaOH |
| 1975 | Introduction of diaphragm electrolyzers |
| 1976 | Introduction of ion-exchange membrane process electrolyzers |
| 1985 |
Introduction of zero-gap technology to electrolyzers |
| 2001 | Increment of the electrolysis cell |
| As of 2022 |
Continuing development of energy-saving technologies Caustic soda production capacity 500,000 t-100% NaOH/yr Number of electrolyzers 30 (4 lines) Estimated value (electrolyzer only) of 1950 kWh/t-100% NaOH |
Related Material
R&D Theme
- Silicone fine particle
"SANSIL™MP-01" - Silica-Titania composite oxide
"SANSIL™FA" - Lead-free transparent
radiation shielding material - Anion conductive
electrolyte materials - Recycling Photovoltaic Panels
- AlN single crystal substrates
- Alkaline water electrolyzer
- Hydrophilic spherical porous silica
with high-purity "Echilsil™" - Hydrophobic spherical silica
aerogel powder "Airlica™"
